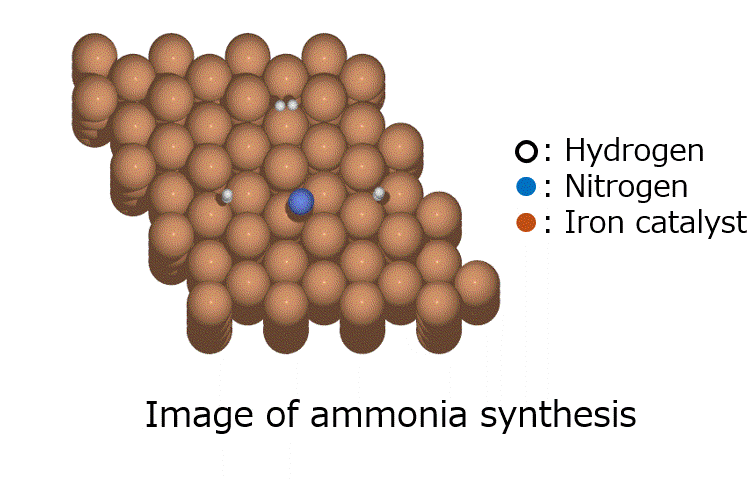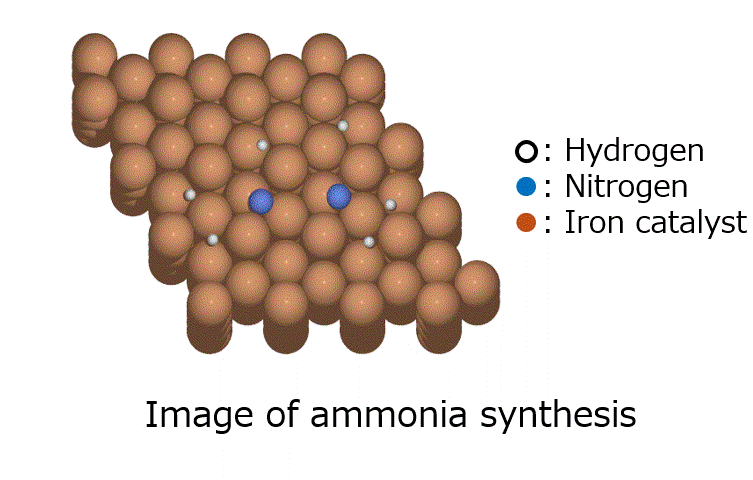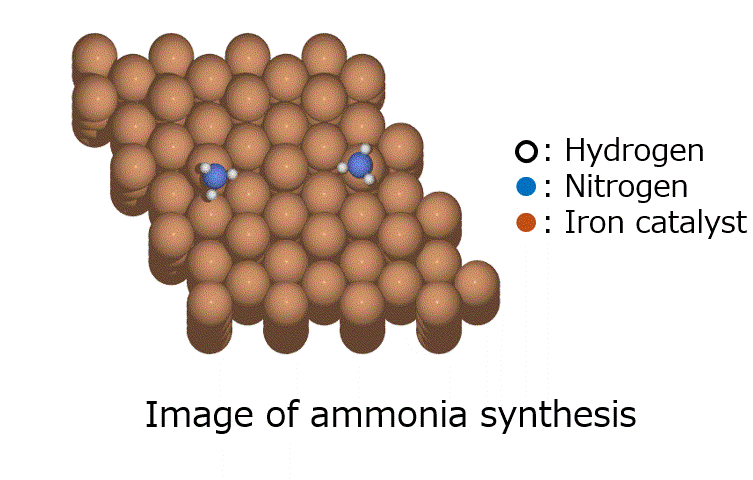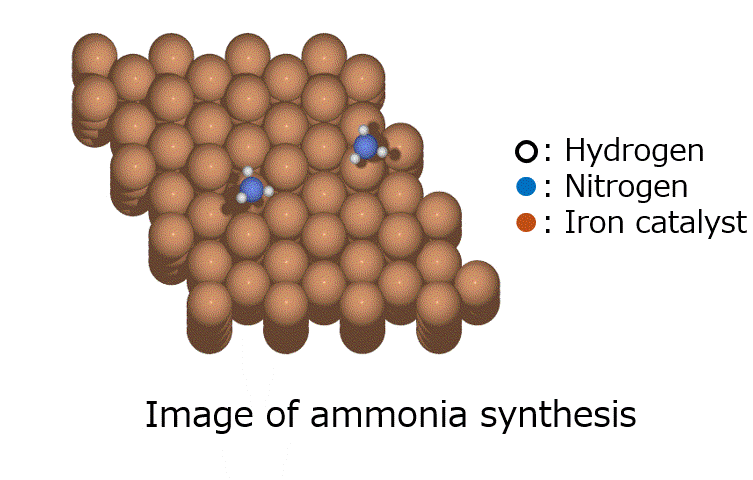
Introduction
The Hildebrand solubility parameter (SP value, δ) is the value obtained by normalizing the heat of vaporization by the specific volume [1]. It is empirically known that compounds with similar values are more likely to be miscible or soluble in each other. Hildebrand SP parameters are easily obtained from relatively easily physical properties such as heat of vaporization and specific volume, using experiments of MD simulations, and thus is used in a wide range of fields, from material development to drug discovery.
In this case study, the Hildebrand solubility parameters of seven small organic compounds were calculated using Matlantis and compared with experimental values [2,3] and results calculated using the GAFF force field [4].
The sample script for this calculation case study are available on matlantis-contrib.
・ https://github.com/matlantis-pfcc/matlantis-contrib/tree/main/matlantis_contrib_examples/solubility_parameter
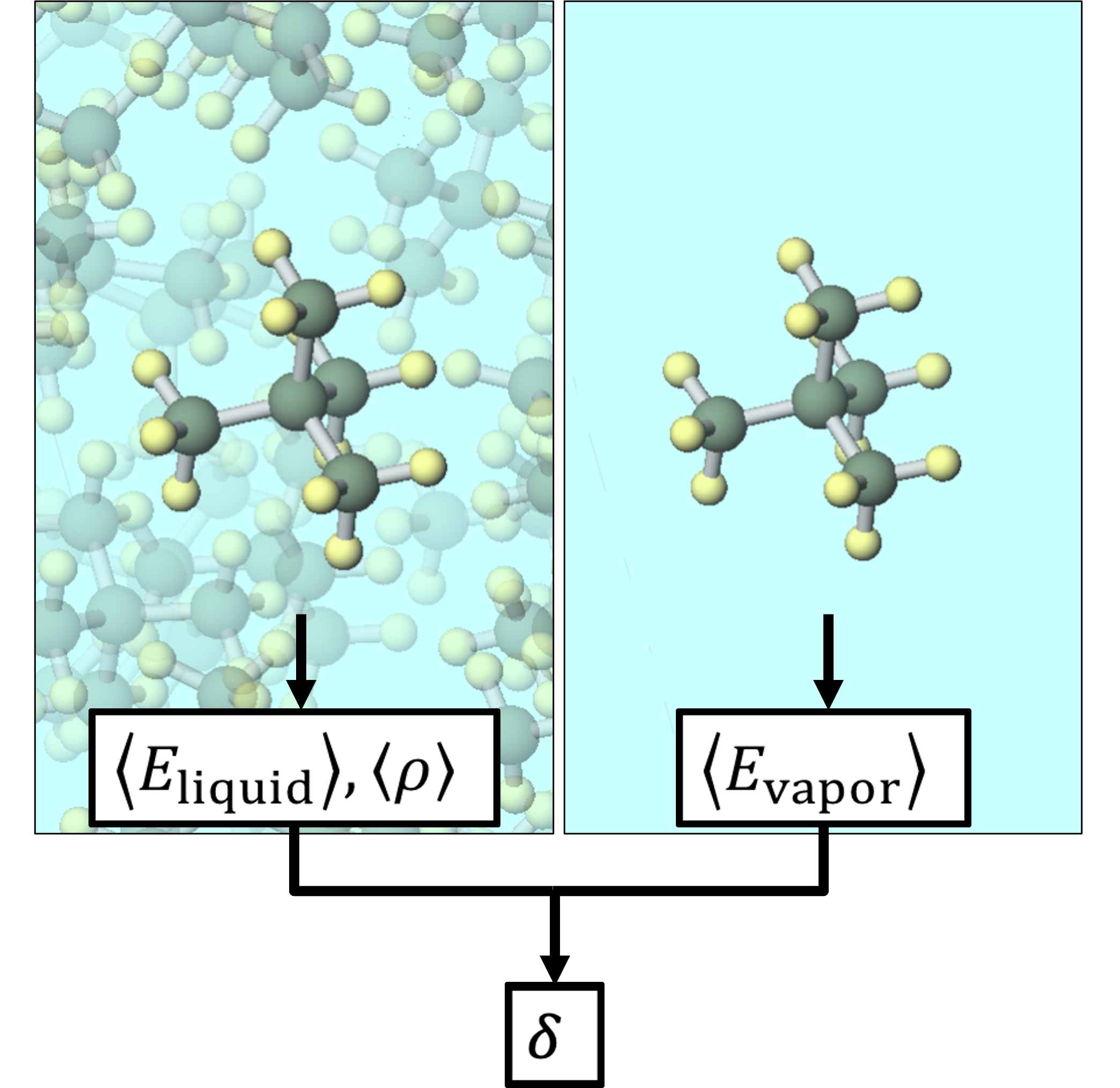
Calculation Models and Methods
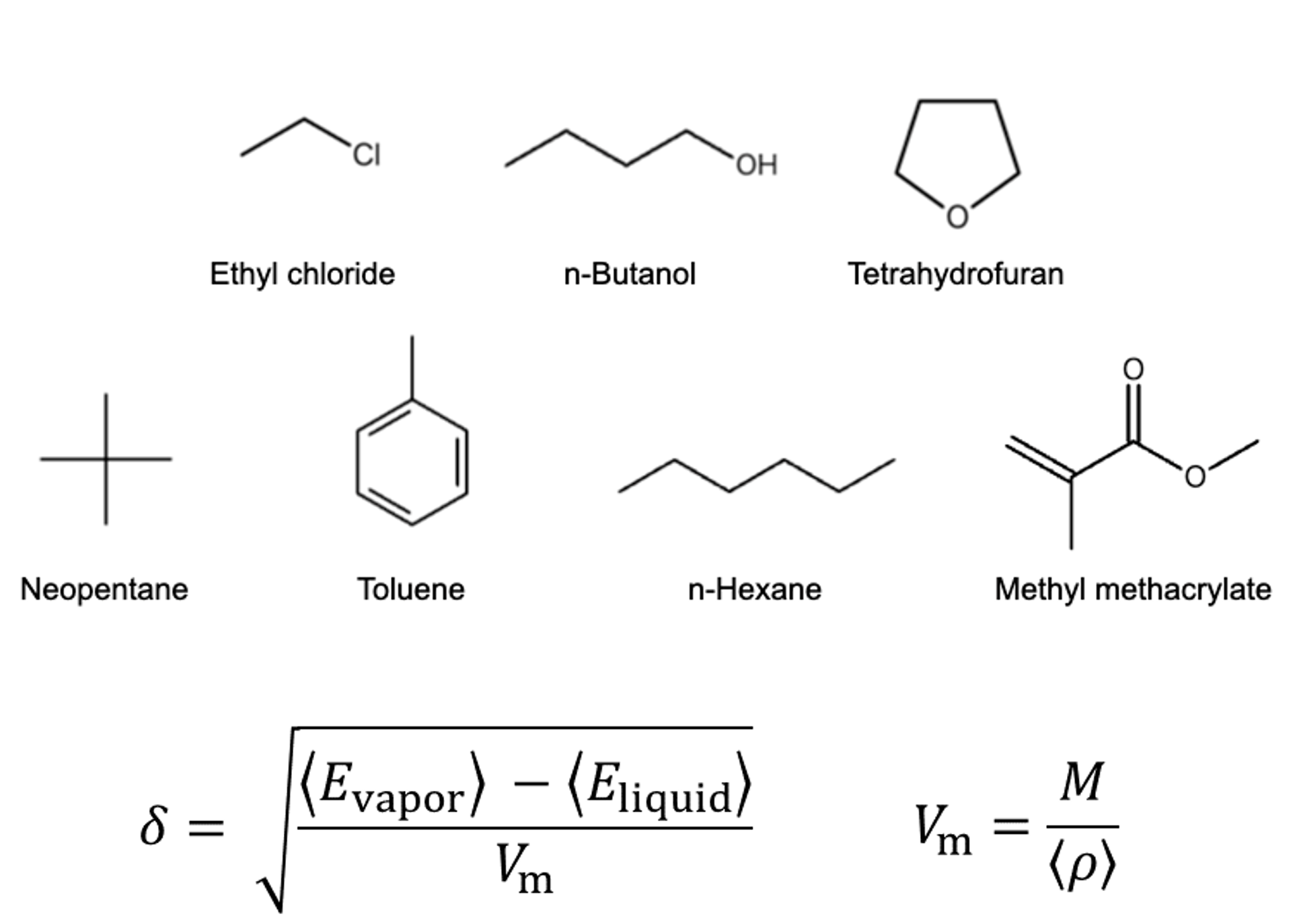
The calculated substances were shown in the figure.
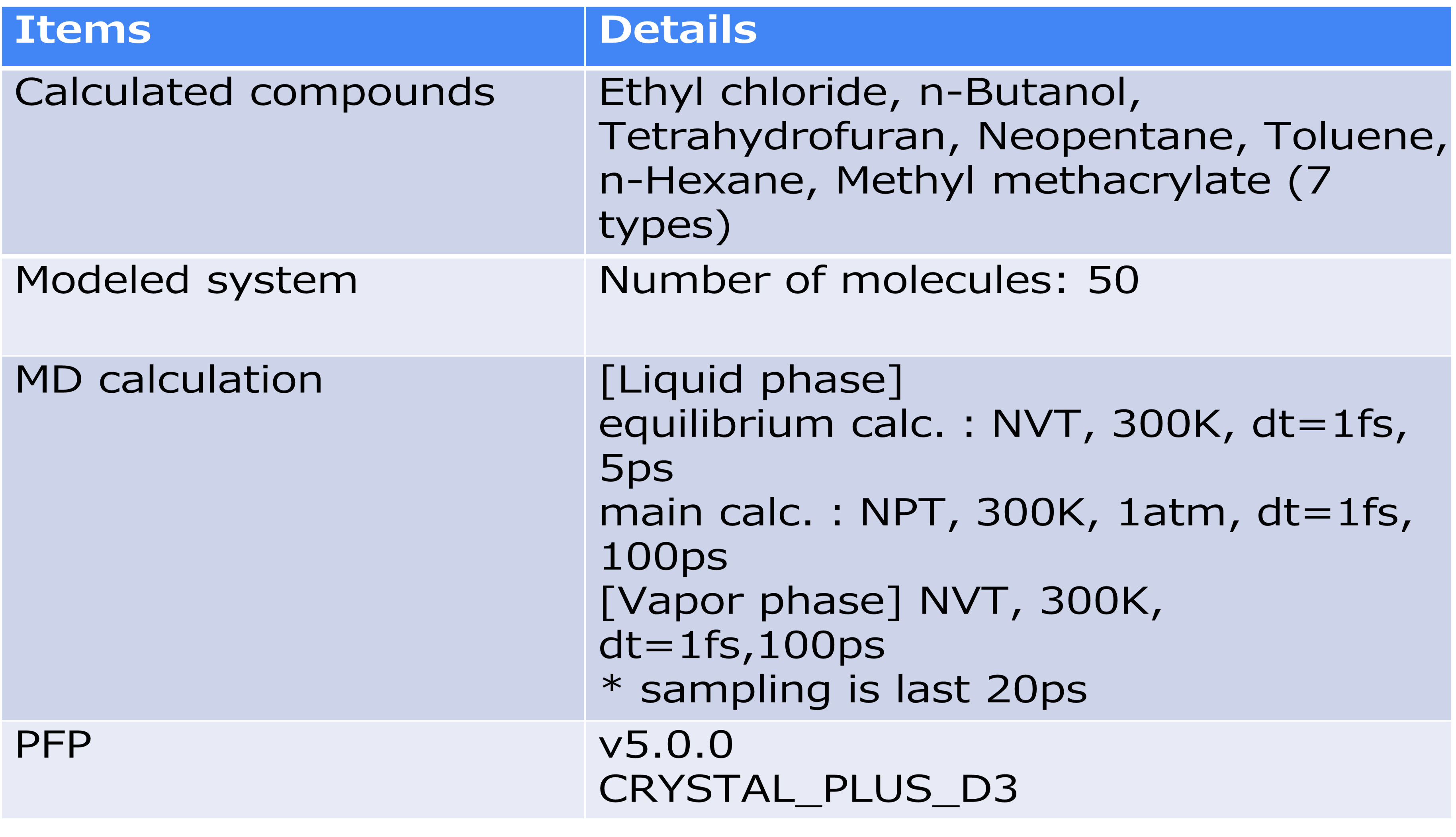
The SP value was calculated according to the formula in the figure. Here, E vapor and E liquid are the potential energies per molecule in the gas phase and liquid phase, respectively, ρ is the average density calculated by NPT calculation, and M is the molecular weight. 〈〉 represents the ensemble average. The calculation conditions for the MD calculation are as shown in the table, and energy minimization calculations were performed before the MD calculation.
To model the systems, Winmostar[5] was used.
Results and Discussion
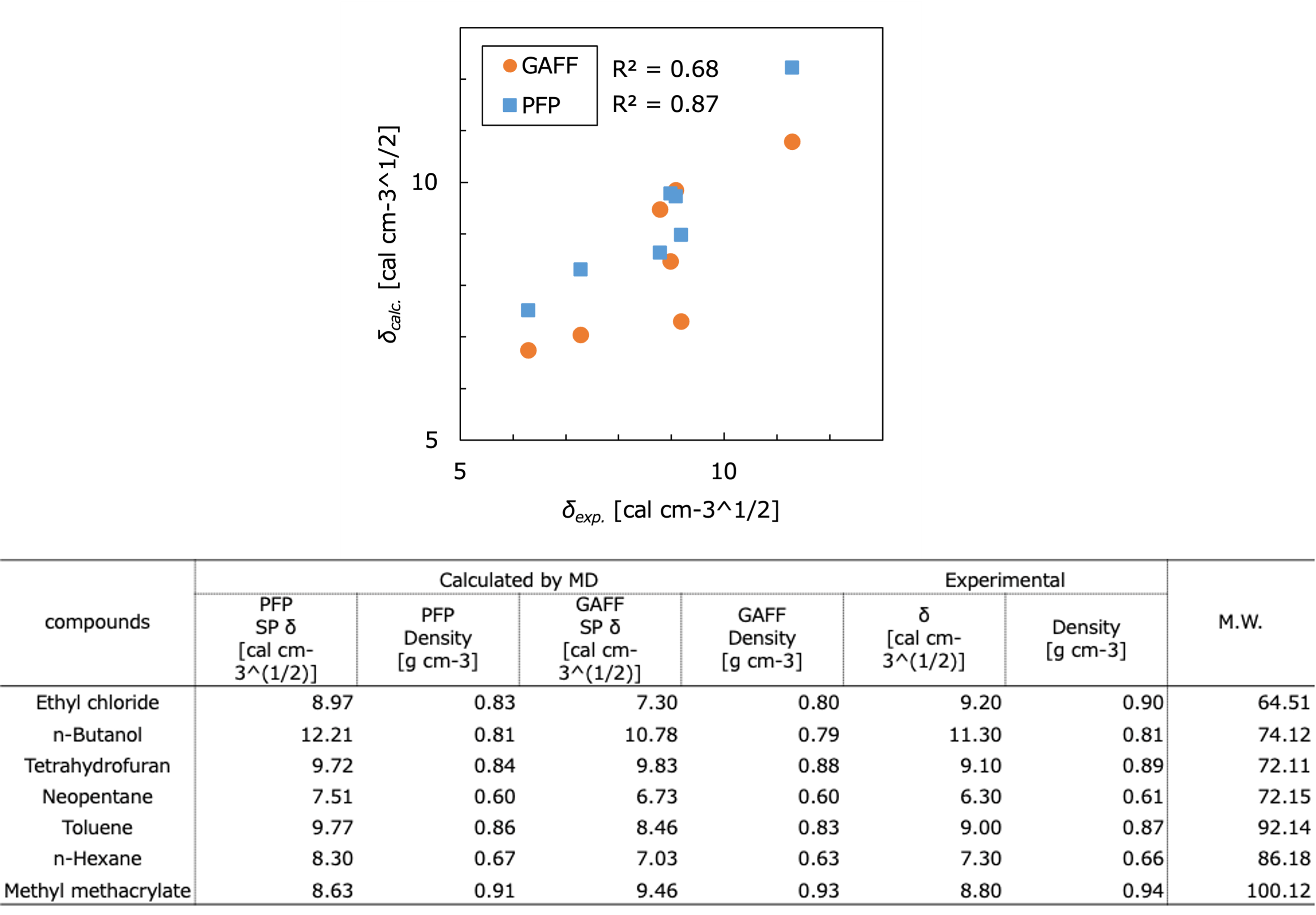
The figure and table show the results of the Hildebrand solubility parameters for each substance compared to the experimental [2, 3] and calculated [2, 4] values, where R2 is the correlation coefficient with the experimental values. In this case study, the SP values obtained using PFP show a better correlation with experimental data compared to those obtained using GAFF.
Simulation Conditions
References
[1] J. H. Hildebrand and R. L. Scott, “Solubility of Nonelectrolytes” 3rd ed., Reinhold, New York (1958) [2] J. Comp. Chem., 25, 1814 (2004) [3] J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 116, 1 (2010) [4] https://winmostar.com/jp/case/calc_hildebrand.pdf [5] X-Ability Winmostar, https://winmostar.com/en/Profile of the case study provider
X-Ability Co., Ltd.

tag
Publication date of this case: 2024.05.10