Cases
We've highlighted some of the most notable examples from user interviews, simulation cases, and research papers. Browse by category to explore the details that interest you.
Featured Cases
Featured Customer Stories
It was impossible to predict based on past experience or intuition.
Creating new combinations and encounters
Kuraray Co., Ltd.Chemical
Combined with AI and experimental data, computational chemistry contributes to raising the level of research and development. “We expect that it can be a powerful tool to compete globally.”
Learn More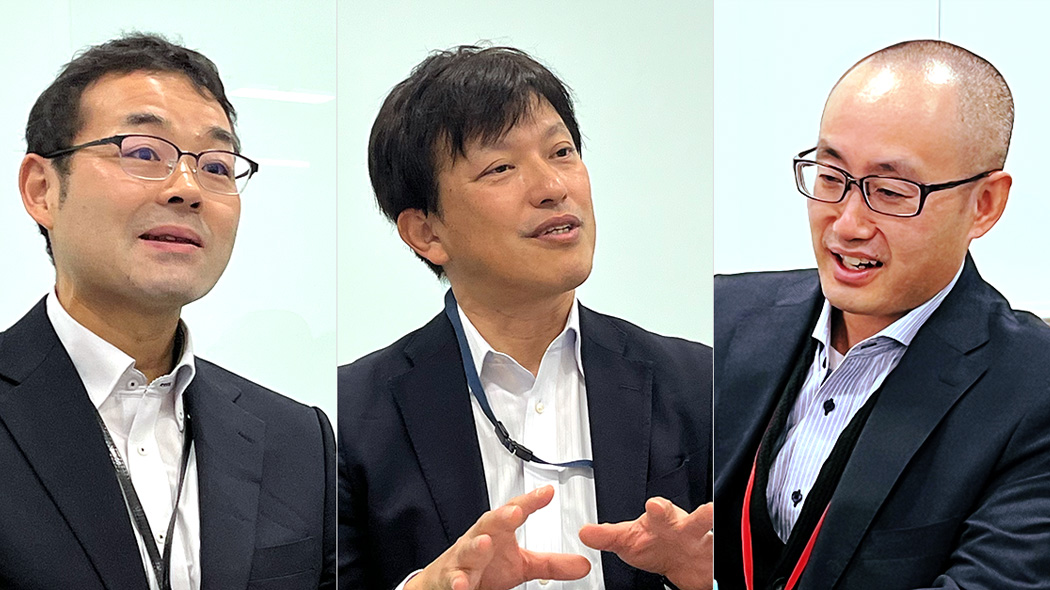
From left to right: Dr. Kamata, Senior Manager of the Planning and Administration Department And Digital Solution Department, Research and Development Division, Mr. Sugoh, General Manager of the Research and Development Division, and Dr. Miura, Manager of the Digital Solution Department established within the Research and Development Division
Featured Calculation Examples
Direct derivation of atomic displacement parameters using NNP-MD
Atomic displacement parameter (ADP)
thermoelectric materials
テーマ概要 結晶構造解析では、原子の熱振動や位置の揺らぎを表す原子変位パラメータ(ADP)が重要な役割を果たします。従来は格子力学計算により求められてきましたが、置換不規則性や分裂サイトを含む複雑な結晶では適用が難しいという課題があり
Learn More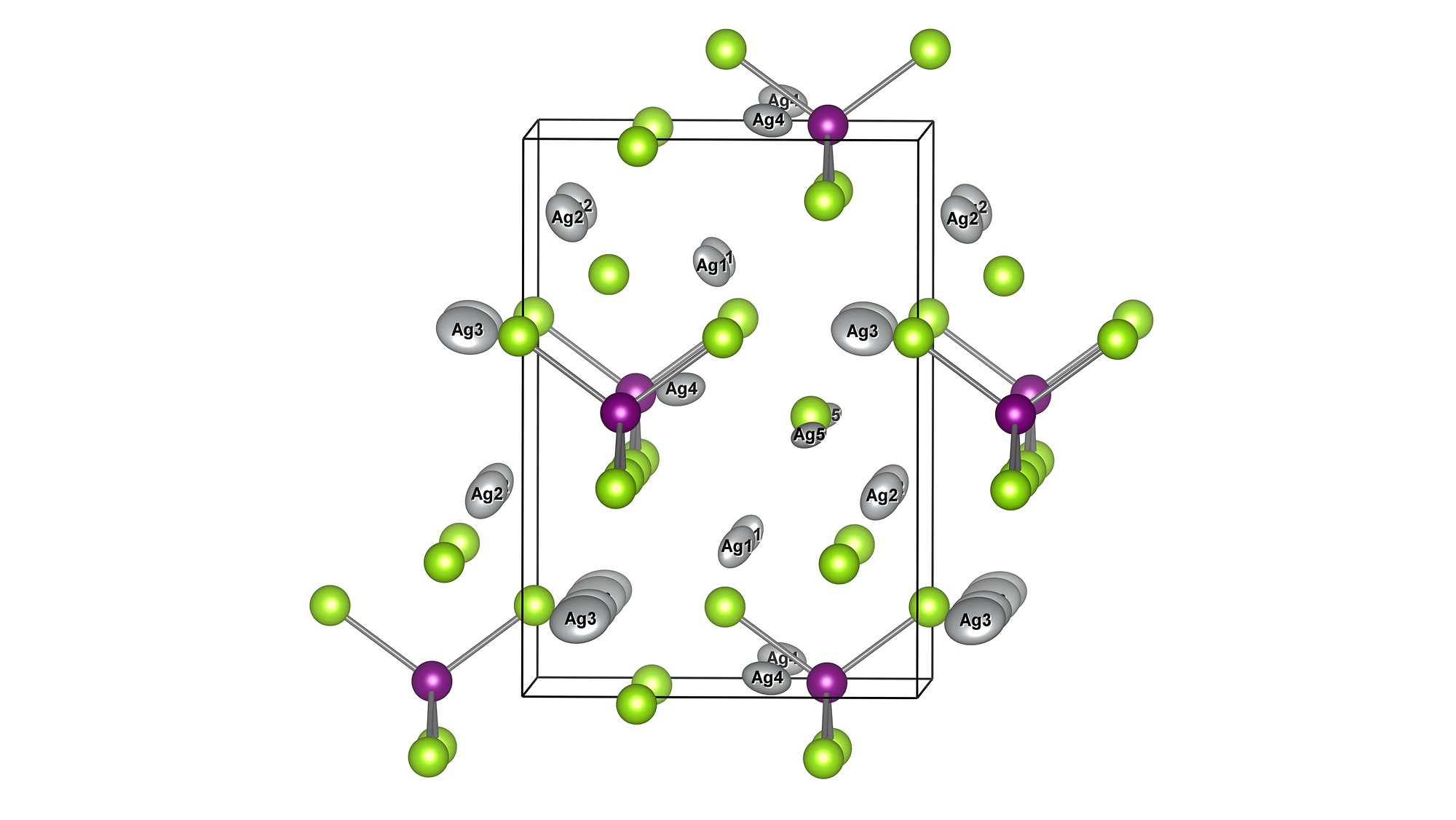
Featured Published Papers
Inhibitor-Assisted Atomic Layer Deposition for Uniformly Doped Ultrathin Films: Overcoming Compositional and Thickness Limitations
Papers using Matlantis
ceramics
Semiconductors
Achieving uniform dopant distribution and fine compositional tuning in atomic layer deposition (ALD) processes remains a significant challenge, particularly for ultrathin films, due to their cyclic nature. This study systematically investigates the inherent limitations of compositional uniformity and the minimum thickness achievable in depositing doped films using ALD. Furthermore, a strategy is implemented to resolve the compositional nonuniformity in the ALD-grown doped films by employing inhibitors. Utilizing Sn-doped In2O3 films as the model system, …
Search for cases by category
List of customer cases
We will introduce the background, challenges, usage methods, and results obtained by companies that have introduced Matlantis. Through real voices from the field, we will provide you with hints that will be useful when considering introducing Matlantis.
List of calculation examples
We will introduce specific simulation examples using Matlantis for various material systems. You can see how high speed and high accuracy calculations are achieved.
List of published papers
This site mainly features papers published by Matlantis users about research using Matlantis, as well as papers about machine learning potential and PFP, which are core technologies of Matlantis.
How to cite
For information on how to cite Matlantis papers and case studies, please see the link below.
Beyond Human Intuition — with Matlantis
Matlantis
Portable Guide
Everything You Need to Know — Features, Benefits, and More
