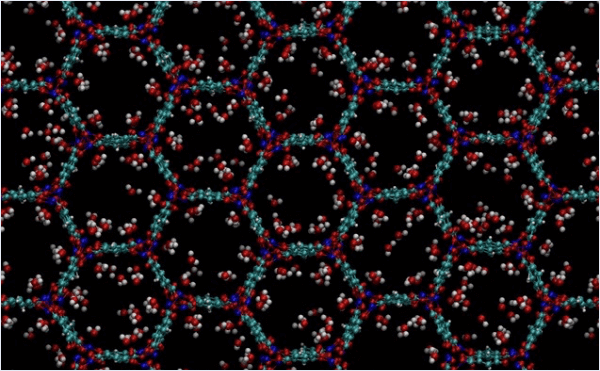
Adsorption and dynamics of H2O molecules in MOF-74Ni
Introduction
Materials with nano-sized micropores, such as zeolites, are used in a wide range of fields as adsorbents, separation membranes, and catalytic materials, and are the subject of extensive academic research. [1]
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are a relatively new class of crystalline materials with nanopore structures, which are attracting attention as next-generation materials due to their unique characteristics.
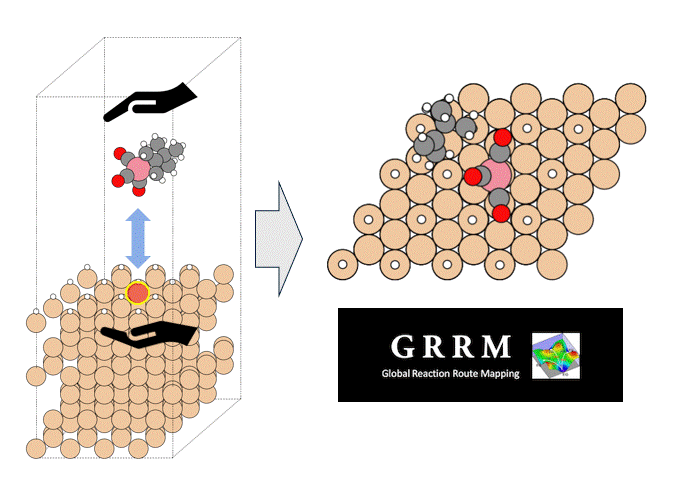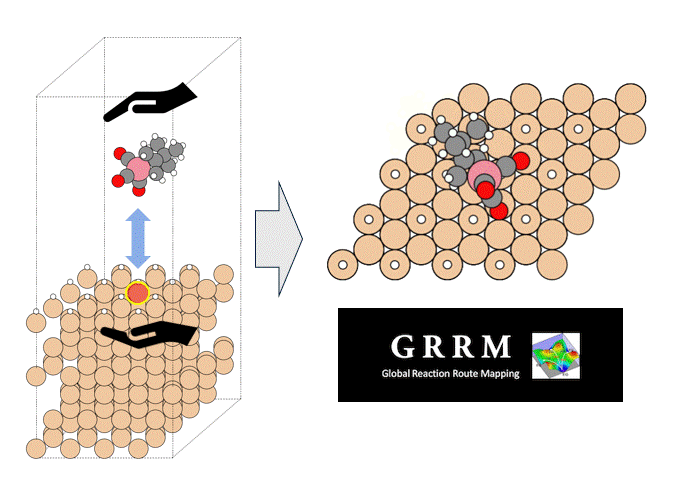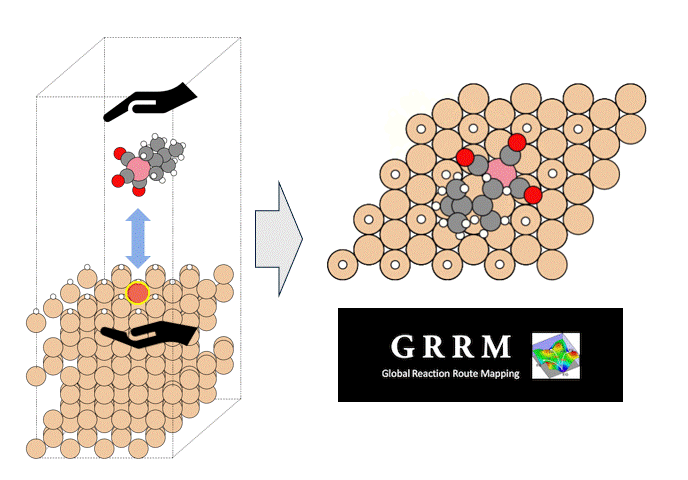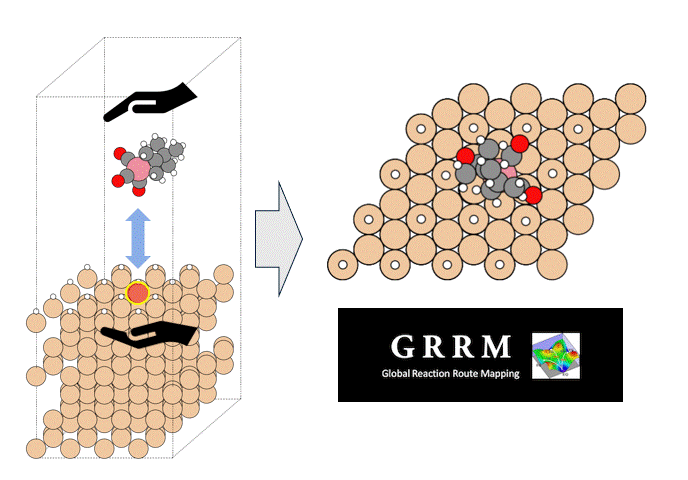
In some MOFs, metal sites are exposed in the pore direction and can be the starting point for chemical reactions such as adsorption and desorption. In this example, we calculate the adsorption energy of H2O using Matlantis. In addition, we look at the behavior of the adsorbed molecules at high temperature.
The sample script is uploaded on github:
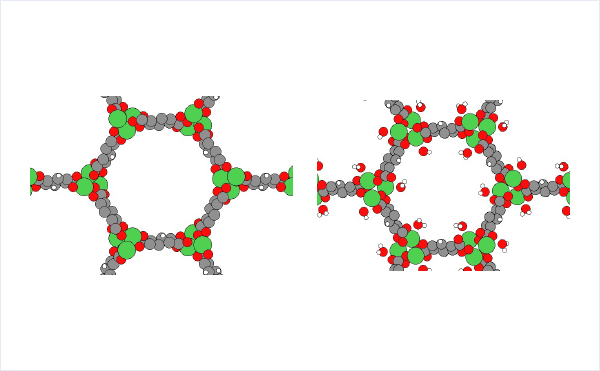
Calculation Models and Methods
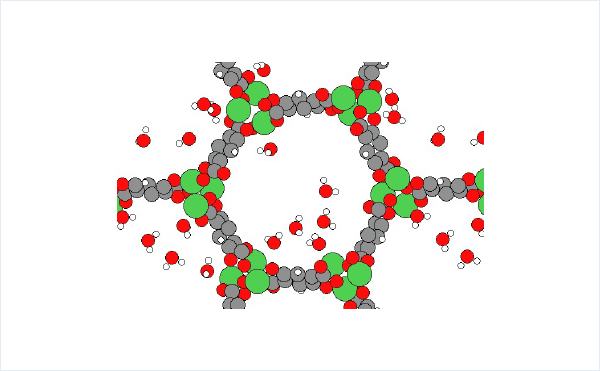
In this section, we calculate the adsorption energy of water molecules in MOF-74 using geometry optimization.
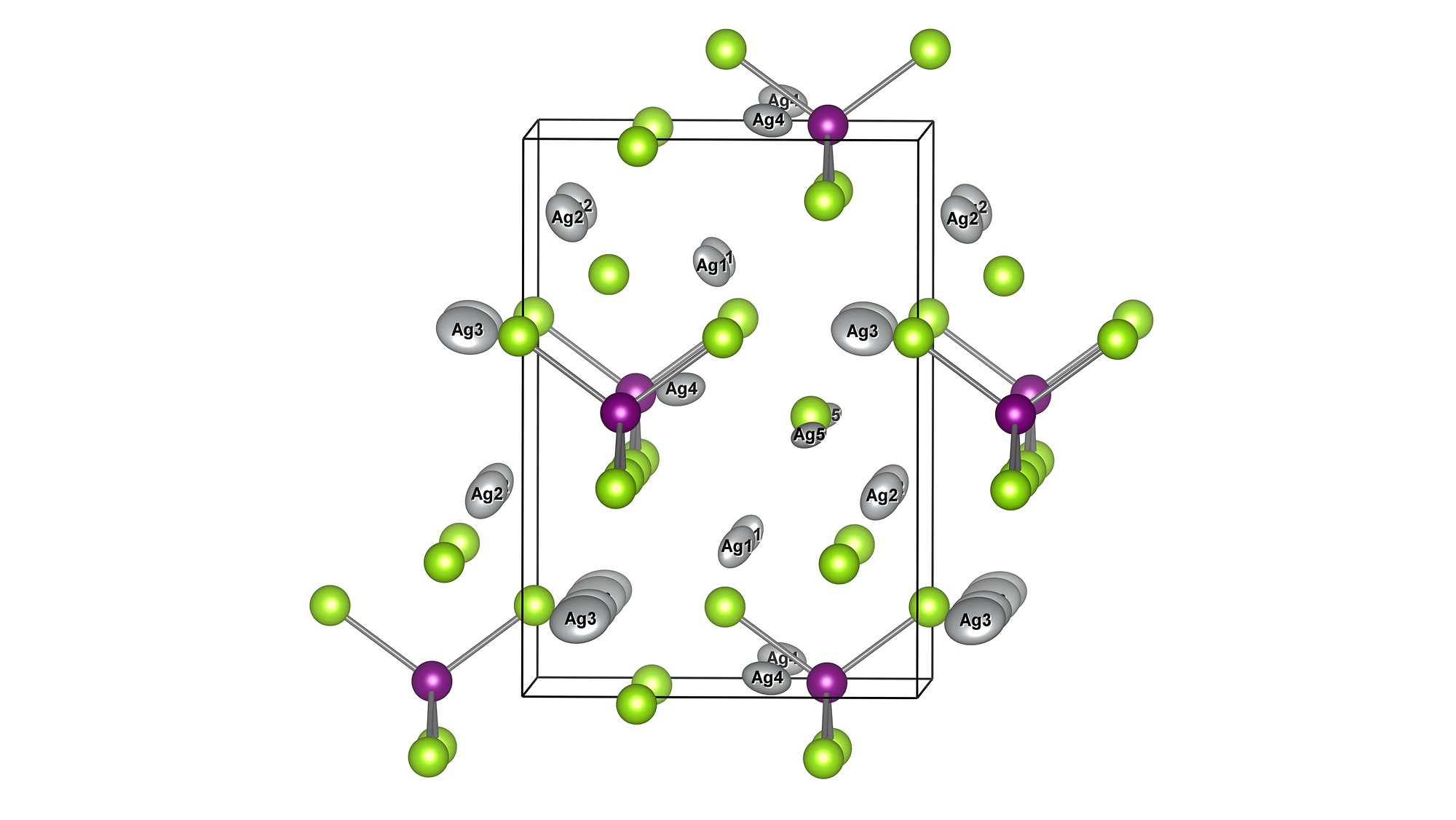
The crystal structure of MOF-74 can be obtained from Cambridge Crystal Structure Database[2]. (hydrated: LEJRIC_288478,dehydrated:LECQEQ_288477).
The structures of isolated water molecule, bare MOF, and MOF with adsorbed water molecules are prepared and used for the rest of the calculations.
Results and Discussion
We were able to calculate the adsorption energy of H2O with the same accuracy as in the previous literature [3]. Molecular dynamics simulations also showed that H2O diffuses between NiO nodes in a hopping manner.
In general, MOFs tend to have large crystal structures of more than several hundred atoms due to the diversity of elemental species and the existence of pore structures. The generalizability and high-speed computation of Matlantis makes it possible to perform studies that would have been highly expensive using conventional methods in a realistic amount of time, making it applicable to materials exploration.
Adsorption energy of water molecules: Ea[kJ/mol] : 48.3 / 64.4 (dispersion force corrected)
Result from previous literature: [3] Ea[kJ/mol] : 61.0 (dispersion force corrected)
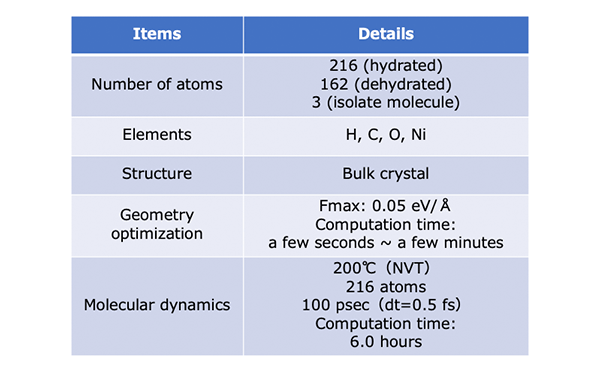
Simulation Conditions
References
[1] OM Yaghi, Science 2013, 341, 1230444 https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.1230444 [2] https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/solutions/data/ [3] F. Bonino, et. al., S. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4957 https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/cm800686ktag
Published: July 1, 2021