Matlantis CSP
Introducing Matlantis CSP - a revolutionary tool that automatically and rapidly discovers stable crystal structures by simply specifying elemental combinations.
What is Matlantis CSP?
Matlantis CSP is a feature that enables high-speed discovery of unknown stable crystals from a vast search space of atomic configurations and compositional combinations within specific elemental systems. By combining Matlantis' core technology - the universal machine learning interatomic potential (PFP) for high-speed calculations - with proprietary algorithms, it overcomes conventional computational limitations and facilitates rapid material exploration.
The Importance of Crystal Structure Prediction (CSP)
CSP refers to the task of identifying energetically stable crystal structures within a given elemental system. In materials research, this approach proves essential primarily in two key scenarios:
- Exploring novel crystal structures: When you want to discover completely unknown stable crystal structures and construct phase diagrams. By comprehensively generating and evaluating numerous atomic configurations and compositions, you can compare them using a common energy metric, enabling discussion of which structures are energetically less stable. This allows you to preemptively exclude structural configurations that would never be experimentally viable, efficiently screening potential stable crystal candidates.
- Evaluating phase stability (element addition to parent structures): When based on a known crystal structure, you want to quantitatively determine how much elemental addition can be made before the phase breaks down and loses stability. By systematically performing element substitutions on the parent structure and evaluating the resulting energy changes and relative stabilities for each composition, you can clearly identify the conditions under which the phase becomes unstable. This enables you to predetermine the compositional range where phase stability is maintained and the boundary where it fails, allowing efficient screening of experimentally unviable compositional conditions.
In materials development, when even a minimal possibility exists, significant time is spent repeatedly conducting synthesis experiments. By using computation to preliminarily determine that certain combinations are "physically impossible" (and thus can be screened out), you can avoid unnecessary experiments and redirect that time toward exploring more promising candidates. This value of "knowing what cannot be done in advance" dramatically improves development efficiency.
Limitations of conventional approaches and Matlantis CSP features
Issues with conventional methods
The traditional CSP approach had three major obstacles.
- Computation time constraints: Structure evaluation through DFT calculations (electronic state calculations) required several hours per structure, while simpler methods produced results with insufficient reliability.
- Search bias: When conducting searches while varying compositions, sampling tended to cluster around certain compositions, making it difficult to conduct comprehensive searches.
- Complex environment setup and configuration: When attempting to explore complex composition spaces, setting input parameters and managing computational environments became extremely complicated, requiring specialized expertise.
Matlantis CSP's Three Core Technical Pillars
To address these challenges, Matlantis CSP incorporates three key technical innovations:
1) High-throughput structure evaluation:
Using PFP enables reliable energy evaluation at an unprecedented speed of seconds to minutes per structure. Additionally, we have implemented a robust system that can reliably perform calculations even for "unusual atomic configurations" that are commonly generated during the CSP process.
2) Comprehensive and highly efficient search across composition space:
Our proprietary algorithm, developed specifically for exploring the entire composition space, enables sampling of diverse structures while maintaining high diversity. This achieves approximately 3-6 times greater search efficiency compared to random sampling, allowing complete exploration of any given composition without missing any potential structures.
3) A parallel processing foundation optimized for the Matlantis environment:
We have implemented memory and parallel processing optimizations specifically designed for operation within the Matlantis environment. This enables high-throughput processing capable of handling tens of thousands of trials in short periods. The significant advantage is that users don't need to build their own environment - they can immediately begin computations without additional setup.
Usability Refined by User Feedback
Matlantis CSP has been continuously refined based on feedback from actual materials development practitioners.
- Intuitive Operation: The interface eliminates the need for specialized computational environment setup, allowing researchers to focus directly on their primary task - materials exploration.
- Comprehensive Examples: Our base code includes practical computational procedures. Users can simply modify element names to match their specific system and immediately begin advanced exploration.
Two Search Modes to Choose From Based on Your Objectives
Depending on your needs, you can switch between the following two modes:
- Global Search: A mode that discovers completely new structures from scratch without making any assumptions about crystal structures. It searches exhaustively for optimal structures by exploring all possible element combinations without prescribing specific atomic numbers or composition ratios.
- Substitutional Structure Search: A mode that assumes a particular parent structure (such as perovskite structure) and explores the stability of substituting elements at specific sites within that structure. This mode is particularly useful for predicting the limits of elemental doping.
Applications
Discovering Unknown New Crystals
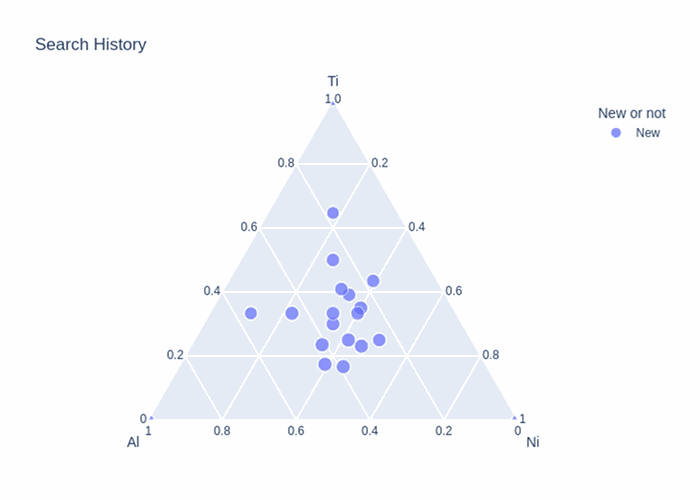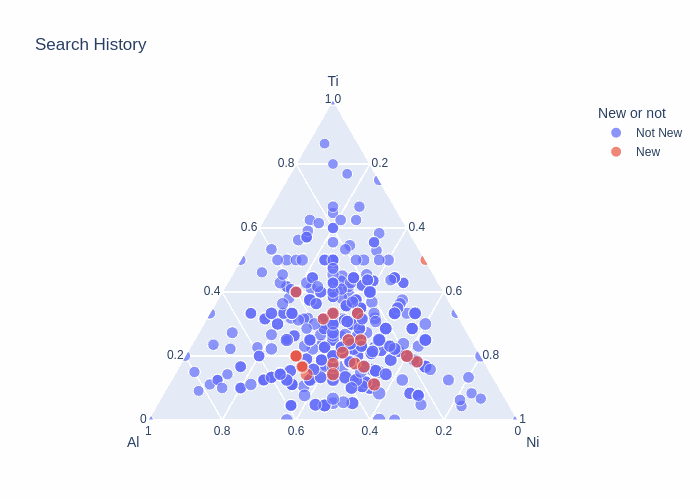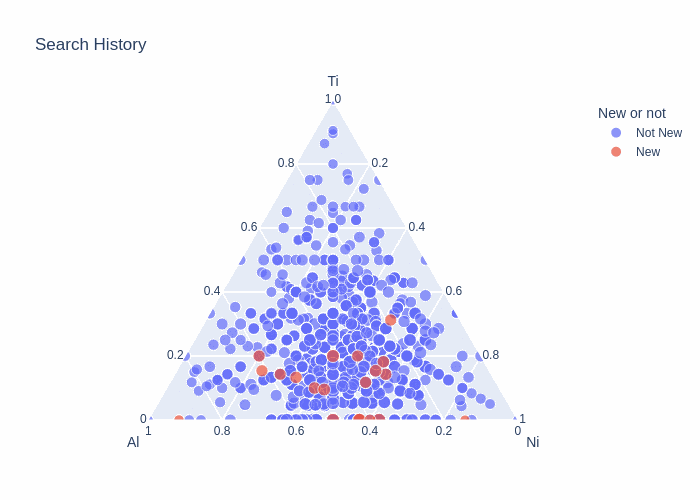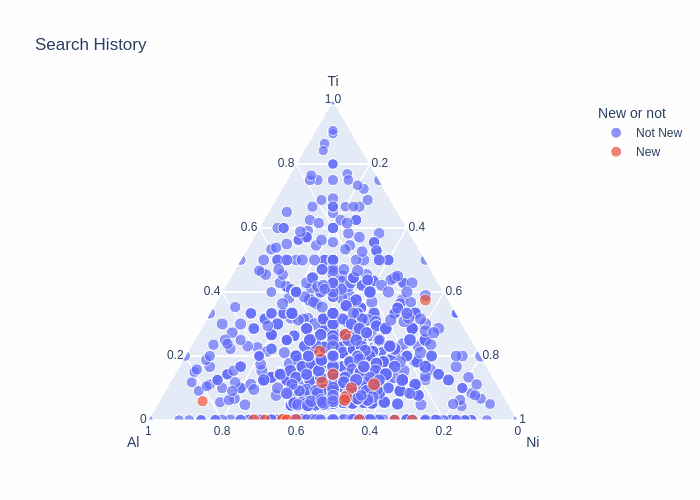
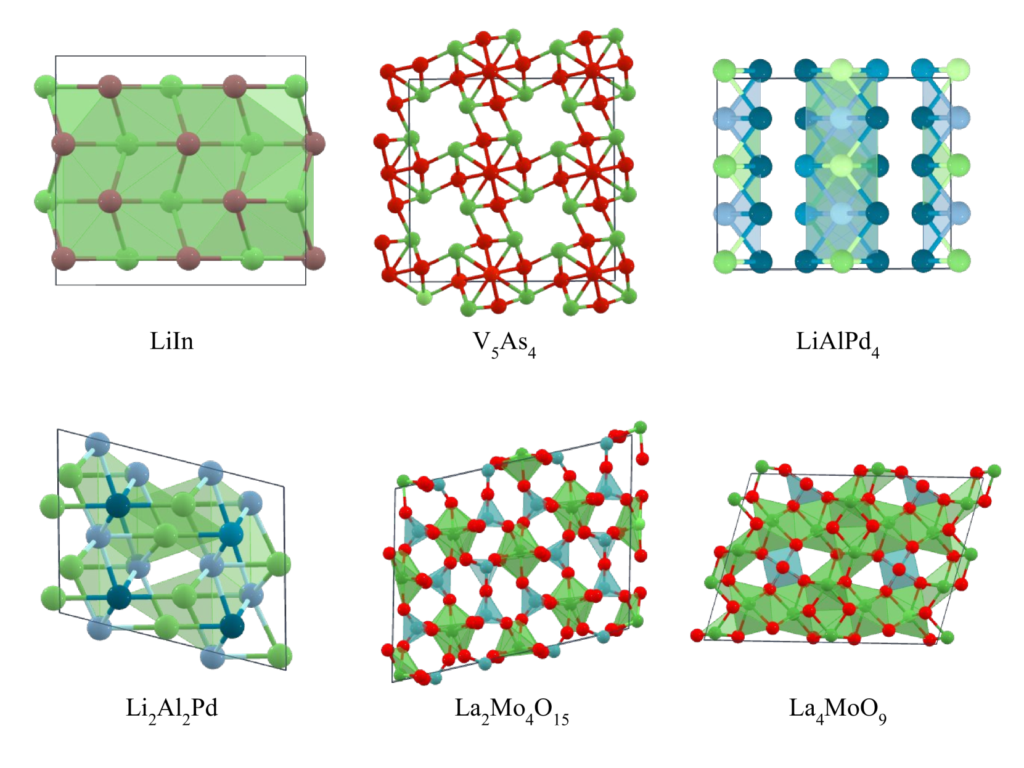
Matlantis CSP has successfully discovered numerous previously unknown stable crystal structures in binary systems like In–Li and As–V, as well as ternary systems like Al–Li–Pd and La–Mo–O, many of which were not reported in existing databases (Materials Project). Through high-speed crystal structure exploration using PFP, we comprehensively searched the vast atomic configuration and composition space, with many of the obtained candidate structures confirmed to be stable even under first-principles calculations (DFT). Among the discovered crystal structures, some have updated the convex hull of the phase diagram, while others represent truly novel structures that don't correspond to any existing crystal prototypes, demonstrating Matlantis CSP's effectiveness for both discovering unknown crystals and updating phase diagrams.
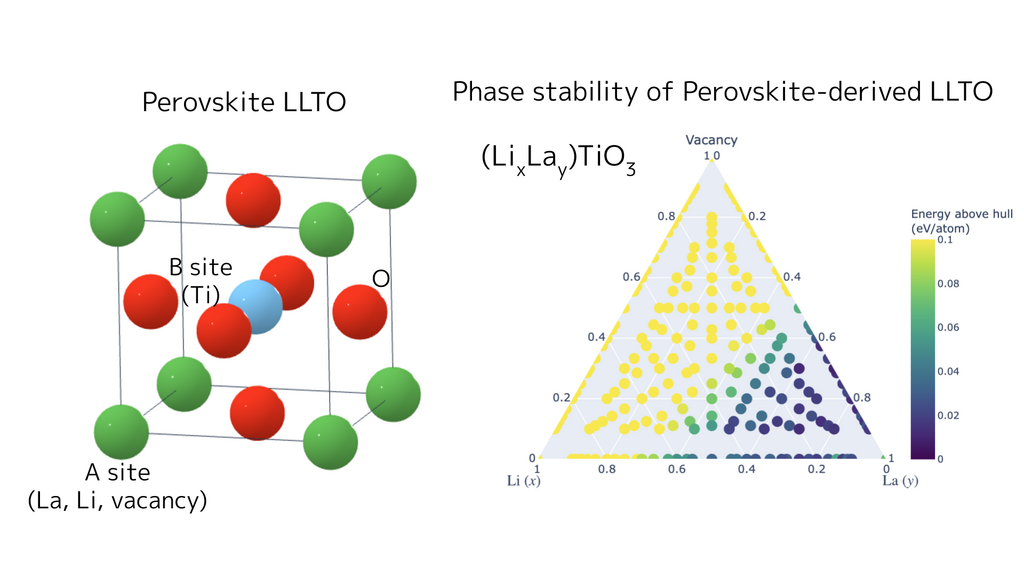
Phase Stability Evaluation via Substitutional Structure Search (Li-Ion Conductor LLTO)
Matlantis CSP is not only useful for discovering new crystals but also for conducting substitutional structure searches based on a given parent structure.For the Li-ion conductive solid electrolyte LLTO (Li–La–Ti–O system), we generated numerous substitutional structures by replacing A-sites with Li, La, and vacancies while using the perovskite structure as the parent structure. By expanding the structures up to 10 times the supercell size, we comprehensively explored diverse configurations of partially occupied Li sites.Using the Li–La–Ti–O system's phase diagram, we evaluated the energy above hull for these substituted structures, enabling quantitative determination—in energy terms—of how much Li or vacancy introduction at the A-site (La) leads to structural instability. This approach allows us to preemptively exclude experimentally unviable compositions and configurations, efficiently screening promising compositional ranges for improving ion conductivity.
*Technical Background: For this functionality's optimization algorithm, we utilize "Optuna™," an open-source automated hyperparameter optimization framework developed primarily by Preferred Networks, with significant enhancements tailored specifically for this software.