過去のお知らせ
学会・講演会
Walter E. Washington Convention Center2025.8.17-21 (USA)
ACS Fall 2025 発表および出展のお知らせ
Matlantis株式会社は2025年8月17日~8月21日(アメリカ東部標準時)に開催される「ACS Fall 2025」に出展いたします。Matlantisからは2名のメンバーがポスター発表を行う他、ブース出展もいたします。またこの他にも社外の組織からMatlantisに関連してポスター発表が1件ございます。内容は以下ご参照ください。
当日のイベントレポートはこちら
ブース出展情報
展示期間 : 2025年8月17日~8月21日(アメリカ東部標準時)
開催場所 : Walter E. Washington Convention Center 801 Allen Y. Lew Place NW, Washington
ブース : 2045
プレゼンテーション詳細
ルーム: Hall C (Walter E. Washington Convention Center)
発表者 1: 米澤 拓孝 (Hirotaka Yonezawa)
セッション: Poster Board #704
日時: 2025年8月20日 6:00 PM – 8:00 PM(アメリカ東部標準時)
部門: Division of Chemical Information (CINF)
セッションタイプ: ポスタープレゼンテーション
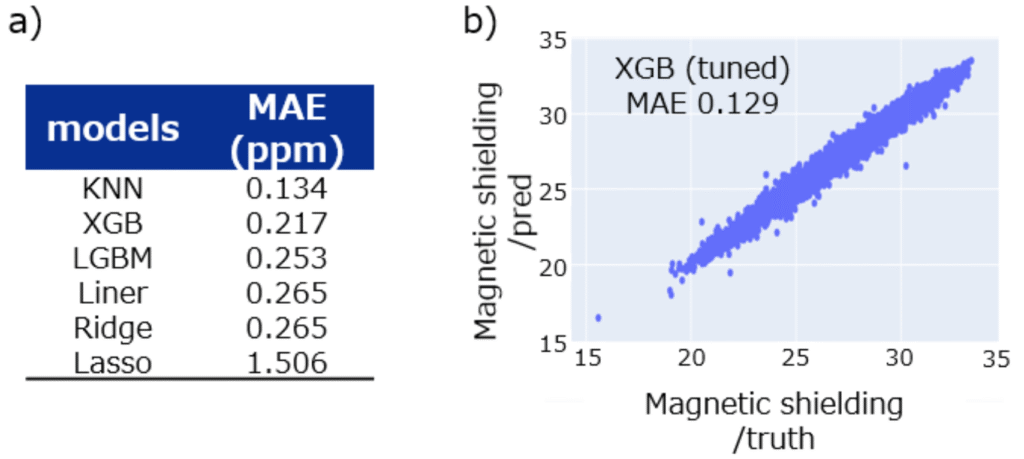
タイトル: NMR chemical shift prediction with PFP descriptor: An application of universal machine learning interatomic potential
概要: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is a crucial technique for identifying the structure of organic molecules. Especially for complex molecules, it is essential to compare simulated spectra with measured data to assign the peaks and determine the structure accurately. This is why the research of chemical shift prediction has long been conducted.
Approaches to chemical shift prediction can be categorized into two types: ab initio techniques and data-driven methods. The latter can be further divided into three categories: additive increment-based, HOSE code, and machine learning.
Approaches have shown comparable good performance. However, these techniques share a common limitation: the representation of the surrounding environment beyond directly connected atoms.
In this study, we propose the approach to create NMR chemical shift prediction models with the descriptors extracted from machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs). This method is superior to previous methods in terms of representing the environment around atoms, especially geometrically distant atoms. This is because MLIPs already account for various intra/inter- and short/long-range atomic interactions and the descriptors can represent the complex interactions and local environments of atoms, providing a comprehensive basis for chemical shift prediction.
米澤 拓孝
Matlantis株式会社 カスタマーサクセスエンジニア。
2018年に東京大学で博士(理学)を取得後、コンサルティングファームにてデータサイエンスによる業務効率化に従事。2024年よりMatlantisに入社。実験化学者でも計算による研究の効率化ができる世界を目指す。専門は有機合成・超分子・光化学。

発表者 2: 名児耶 彰洋 (Akihiro Nagoya)
セッション: Poster Board #928
日時: 2025年8月19日 6:00 PM – 8:00 PM(アメリカ東部標準時)
部門: Division of Computers in Chemistry (COMP)
セッションタイプ: ポスタープレゼンテーション
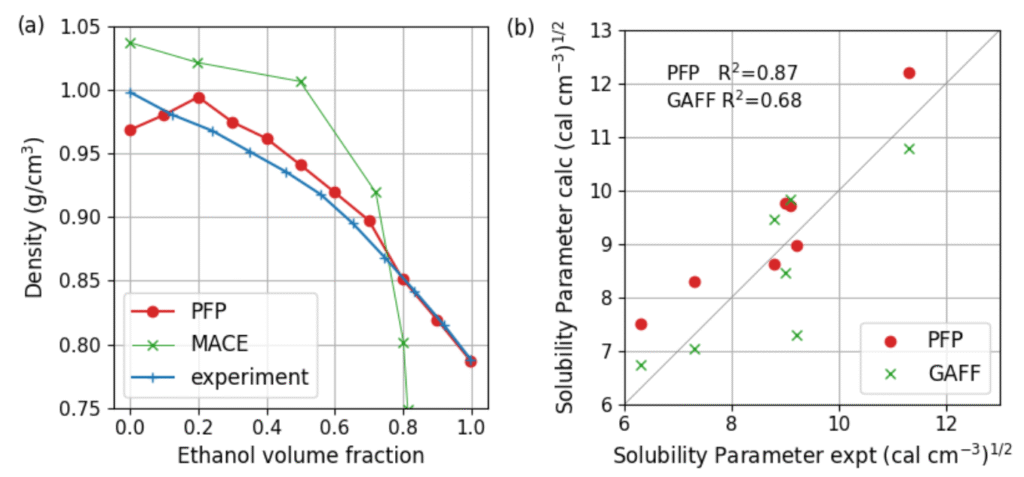
タイトル: Application of a universal graph neural network potential for molecular dynamics of liquid phases
概要: Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are essential tools for studying the structure and dynamics of liquid phase in chemistry, materials science and biophysics. Applications include solvation structure analysis, ion transport in electrolytes, phase equilibria, interfacial behaviour and diffusion processes. However, classical force fields often lack the accuracy required to capture complex interactions, such as chemical reactions at solid/liquid interface, while ab initio MD is too computationally expensive.
Recent advances in machine learning potentials (MLPs) have opened new possibilities for liquid phase simulations. MLPs have been successfully applied to a number of liquid systems achieving DFT accuracy at much lower cost. MLPs allow MD simulations of complex phases that are inaccessible using quantum methods. On the other hand, the atomic configuration may be outside the training data set during long MD simulations, leading to error accumulation or inaccurate physical behaviour. The Preferred Potential (PFP), integrated into Matlantis™, is a recently developed universal graph neural network (GNN) potential. PFP achieved a high level of accuracy and robustness due to its training on the huge DFT dataset. It offers superior applicability, transferability, and consistency across a broad range of systems without fine-tuning for specific systems. Thus, it is widely used for various applications such as catalysts, battery materials, metals and polymers.
In this study, we validated the accuracy of PFP for liquid phases. The solubility of organic liquids was evaluated using the Hildebrand solubility parameter derived from MD simulations. PFP agrees well with experimental data and predicts solubility more accurately than the GAFF force field. Furthermore, we validated the density of a water-ethanol mixture, with PFP showing good agreement with experimental data. Note that the underestimation for pure water is due to known errors in the PBE data set. It can be improved by training the model with more sophisticated functional. The results demonstrate that PFP is suitable for practical MD simulations and facilitates materials development.
名児耶 彰洋
Matlantis株式会社 シニアアプリケーションサイエンティスト。
大阪大学を卒業後に株式会社豊田中央研究所の研究員として勤務。太陽電池材料、燃料電池白金触媒、二次元材料の第一原理計算や高分子の古典MD計算を使用したMIなどの研究に約15年間従事した。その後、ENEOS株式会社の中央技術研究所を経てMatlantisに入社。現在は主に電池材料や金属材料に関わる計算に携わっている。

Matlantisに関する社外の講演
2025年8月18日
セッション: Chemical Reaction Networks, Retrosynthesis, and Reaction Prediction
日時: 2025年8月18日 5:20 PM – 5:40 PM(アメリカ東部標準時)
部門: Division of Computers in Chemistry (COMP)
ルーム: Hall E – Room 25 (Walter E. Washington Convention Center)
セッションタイプ: 口頭
タイトル: Automated generation of reaction pathways using neural networks
発表者: Akihide Hayashi, So Takamoto, Ju Li, Hirotaka Akihide, Daisuka Okanohara
組織: Preferred Networks, inc. & Massachusetts Institute of Technology
2025年8月19日
セッション: Poster Board #922
日時: 2025年8月19日 6:00 PM – 8:00 PM(アメリカ東部標準時)
部門: Division of Computers in Chemistry (COMP)
ルーム: Hall C (Walter E. Washington Convention Center)
セッションタイプ: ポスタープレゼンテーション
タイトル: r2SCAN level universal neural network potential for molecules, crystals and surfaces
発表者: Chikashi Shinagawa, So Takamoto, Daiki Shintani, Katsuhiko Nishimra, Kohei, Shinohara, Shigeru Iwase, Yuta Tsuboi, Ju Li
組織: Preferred Networks, inc. & Massachusetts Institute of Technology
学会公式情報はこちら (外部サイト) >> ACS Fall 2025
公開日:2025.08.13



